Did Enbridge Use Toxic Chemicals to Clean Up Their Oil Spill in Kalamazoo?
On Sunday, July 25, 2010, Enbridge Line 6B ruptured near Marshall, Mich. and released more than one million gallons of Canadian diluted bitumen into Talmadge Creek and the Kalamazoo River. Illustration by Catherine Mann for InsideClimate News.
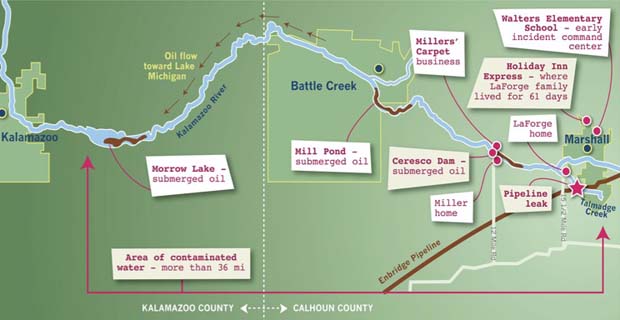
[dropcap]I[/dropcap]t’s been three and a half years since Enbridge’s Line 6B pipeline ruptured in Marshall, Michigan, leaking more than843,000 gallons of diluted tar sands bitumen into the Kalamazoo River. It was the largest on-land oil spill in the history of the USA, and remains, so far, as the largest spill of tar sands oil ever. Yet despite Enbridge’s immense, ongoing clean-uo operation, which has spanned more than three years, cost over a billion dollars, and removed significantly more oil from the river than the company will admit it spilled, those living in Enbridge’s sacrifice zone have more questions than answers—even as most areas of the river have been re-opened for public use. High on the list of concerns is a chilling refrain: What are these chemicals that work crews have been dumping into the river in massive quantities, and are they dangerous?
At first, eyewitness accounts of workers spraying what appeared to be chemicals at the ground or out of boats, pouring unidentified liquid detergents into the water, or dumping hundreds of truckloads of sand-like powder into the river from dump trucks, became subjects of intrigue and speculation among community members and local activists. Another telltale sign was mysterious, oily foam floating on the water, and frequent helicopter deliveries of cargo to back-wooded areas of the Kalamazoo. There was an air of secrecy amongst those who carried out the work. They conducted large operations at night and told the residents that they were only spraying water or pesticides to repel mosquitos. Michelle Barlond-Smith, a former resident of the heavily impacted Baker Trailer Park, told me that “a lot of us thought they were hiding and covering up stuff, trying to bury it, the oil. The first time I heard about it was probably a month into the spill. One of my neighbors said, ‘Hey Michelle, they’re back there, they’re spraying something on the ground.’ And I’d go racing back there and the minute they would see me they would take off, running—literally sometimes running.”
Craig Ritter, an intrepid explorer of the Kalamazoo and a fisherman turned activist, told me similar stories. “Along with other residents, we were seeing a lot of dump trucks backing up to the river and dumping product in, which we thought at the time was probably sand,” he said. He had assumed that the trucks were there to “put sand back into the river [in order] to fill the holes that they were dredging,” but discovered that the trucks weren’t carrying sand at all. “When I did get a chance to get close to one of those trucks it had a real strong herbicide, almost pesticide, chemical smell to it,” Ritter explained. Like Michelle Barlond-Smith, Ritter had also sensed that Enbridge was hiding something. As a result of his repeated explorations of the Kalamazoo, he found himself occasionally “followed around by personnel vehicles,” and noticed “cars pulled up, and kind of eyeballing, if not having a camera out and taking pictures of me” when he lingered in sections of the river that had already been re-opened for public use.
![]() To read complete story – click here […]
To read complete story – click here […]
NOTE: Enbridge is Canada’s largest transporter of crude oil, with approximately 5,372 miles of crude pipeline, delivering on average more than 2.2 million barrels per day of crude oil and liquids.







